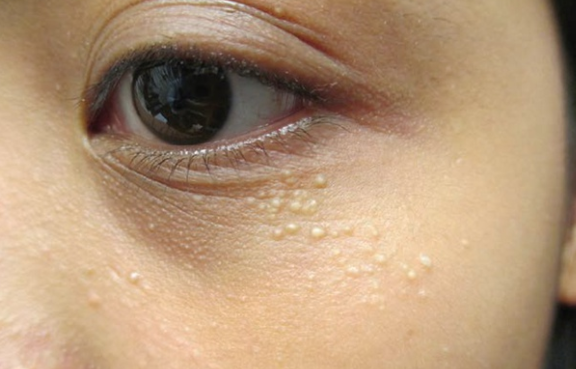
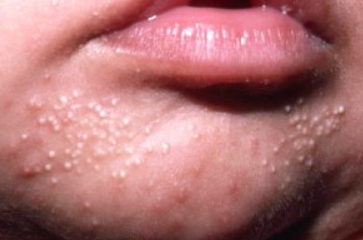
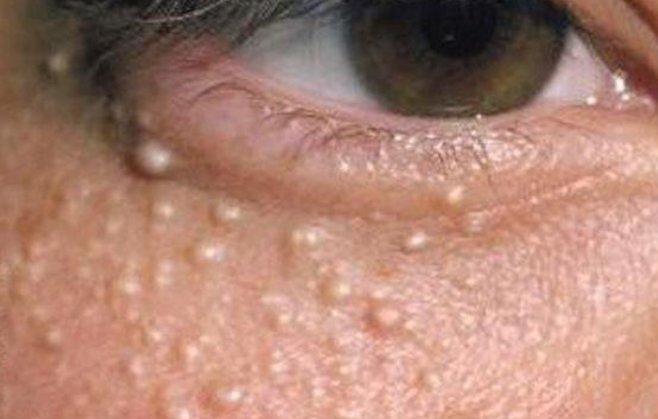
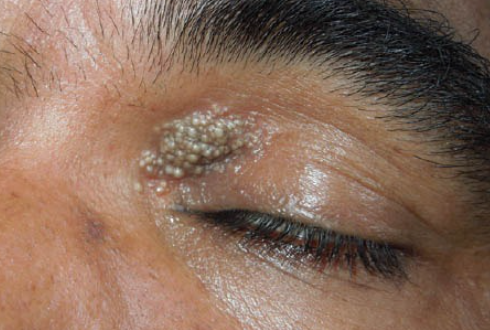
Milium (milia) is a small epidermal cyst containing keratin, which typically occurs in newborns and can also develop in certain dermatoses and after trauma. The ICD-10 code is L72.8.
Milia can occur in all ages and races, but is most commonly observed in newborns. Milia may also occur in certain dermatoses, inherited disorders, and after trauma (see Classification). Milia develop when the protein keratin gets trapped under the skin.
Classification:
Primary Milia:
- Congenital Milia (present at birth)
- Benign Primary Milia in children, adolescents, and adults
- Milia en plaque
- Grouped nodular milia
- Multiple eruptive milia
- Depigmented nevus with milia
- Milia associated with inherited disorders:
- Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome
- Rombo syndrome
- Brooke-Spiegler syndrome
- Atrichia with papular lesions
- Vitamin D-dependent rickets type IIA
- Basal cell nevus syndrome
- Generalized basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome
- Absence of fingerprints-congenital milia syndrome (Baird syndrome)
- Nicolau-Balus syndrome
- Hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy
- KID syndrome
- Loeys-Dietz syndrome.
Secondary Milia:
- Post-traumatic (on sites of abrasions, sunburns, postoperative wounds, dermatoses, cryotherapy)
- Milia associated with dermatoses (porphyria cutanea tarda, bullous epidermolysis, bullous pemphigoid, herpes zoster, dermatitis herpetiformis, discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen sclerosis, lichen planus, Sweet's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, congenital syphilis, skin calcinosis, leprosy, leishmaniasis, phototoxic reactions, bullous amyloidosis)
- Drug-induced milia (steroid atrophy, isotretinoin, cyclosporine, penicillamine)
Pseudomilia: orofaciodigital syndrome type 1, inherited trichodysplasia (Marie-Unna hypotrichosis), anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia - which resemble milia clinically but not histologically.
Newborn Milia
Milia in Children, Adolescents, and Adults
Milia en Plaque
- Hydrocystoma
- Syringoma
- Trichoepithelioma
- Eruptive vellus hair cysts
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Sebaceous hyperplasia