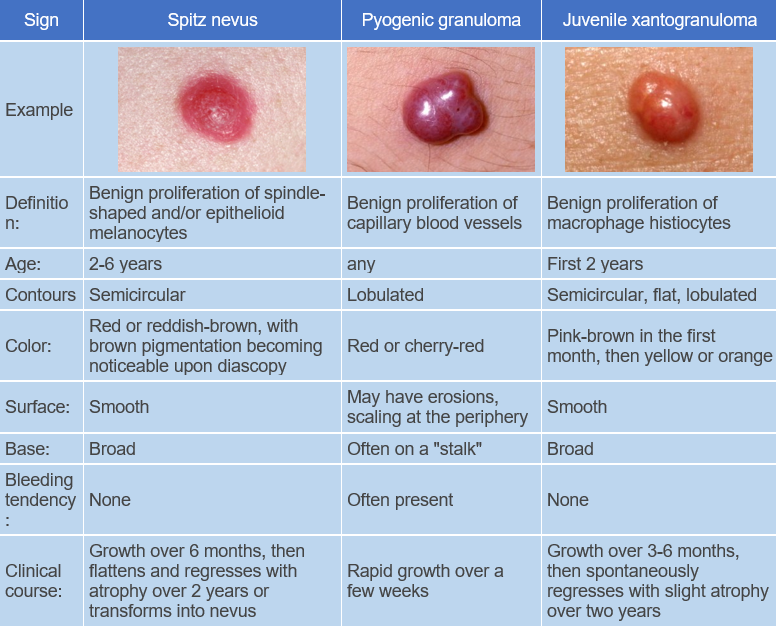
Pyogenic granuloma (Lobular capillary hemangioma) is a benign post-traumatic proliferation of capillary blood vessels. ICD-10 code: L98.0
It can occur at any age but is more common between 10-40 years old and is not significantly affected by ethnicity. It is slightly more common in females, especially when localized in the oral cavity.
The etiology and pathogenesis are not completely understood. The role of certain viruses (papillomaviruses, herpes viruses), microtrauma (microinjuries), hormonal imbalances (more common in pregnant women and during menopause), medications (anticancer drugs, antiretroviral drugs, retinoids, immunosuppressants, oral contraceptives, epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors) are being considered. In recent times, importance is attached to sporadic mutations in the BRAF gene (v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 - a gene encoding proteins that regulate cell growth signaling pathways).Typical pyogenic granuloma
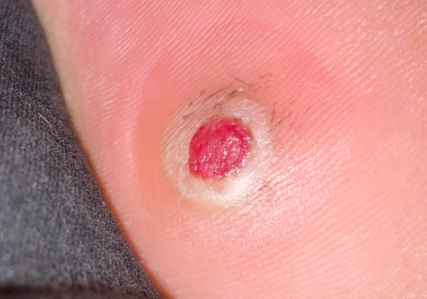
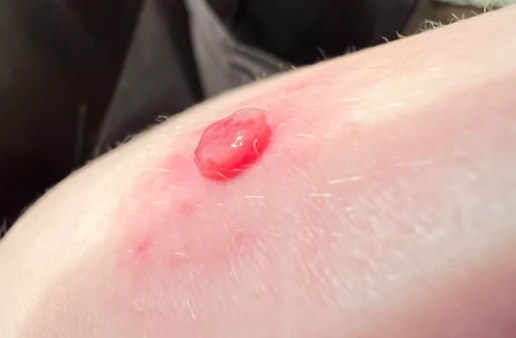
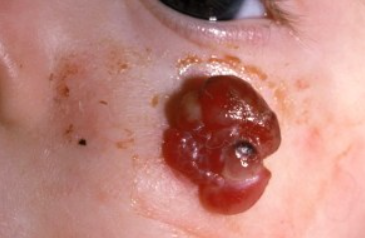
Presents as a single papule up to 1 cm in diameter with a shiny surface, firm elastic consistency, and variable color ranging from light gray to dark red. It is characterized by rapid growth (within a few weeks) followed by stabilization, The lesion may acquire a lobulated, mushroom-like, or perpendicular shape. The condition usually progresses without subjective sensation, but the growth may bleed easily upon trauma, often resulting in erosions and ulcers covered with crusts. The eroded surface often has a "granular" appearance. The presence of a rim around the lesion is characteristic when located on the palms and soles, where they are often traumatized.
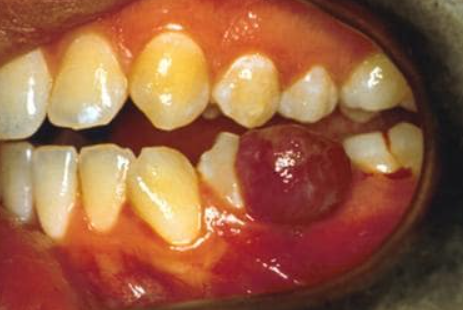
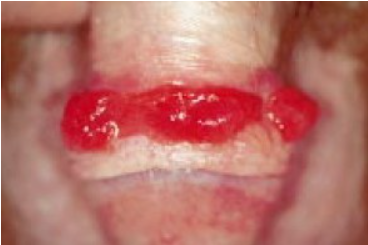
The eruptions can occur anywhere, but they are most commonly found on the dorsum of the hands, feet, and fingers due to their frequent trauma.Oral pyogenic granuloma
Giant pyogenic granuloma
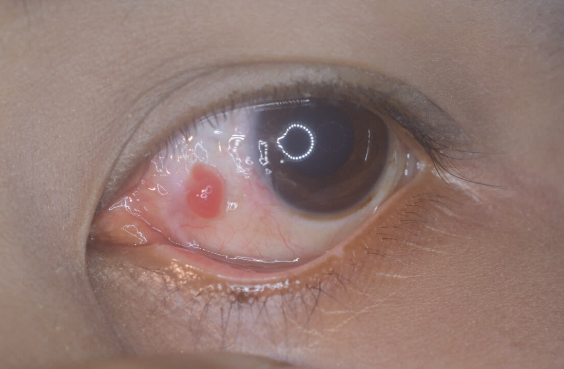
Ocular pyogenic granuloma
Genital pyogenic granuloma
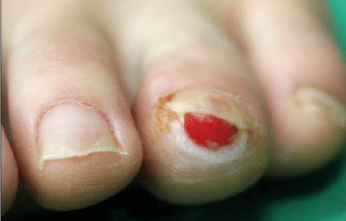
Subungual pyogenic granuloma
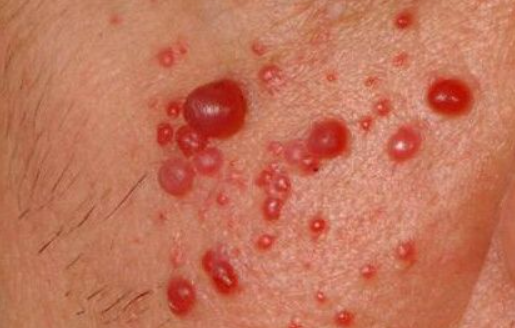
Multiple pyogenic granuloma
- Kaposi Sarcoma
- Hemangioma
- Amelanotic melanoma
- Bacillary angiomatosis
- Cherry Angioma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
- Metastases
- Glomus Tumor
- Angiosarcoma
- Nevus Spitz
- Angioleiomyosarcoma
- Clear Cell Acanthoma
- Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
- Acrochordon (Skin tag)
- Odontogenic Fibroma
- Juvenile Xanthogranuloma
- Spider Angioma
- Ossifying Fibroma
- Surgical excision and cryotherapy
- Curettage
- Sclerosing therapy
- Laser therapy (ND-YAG, CO2, diode with wavelengths of 808-980 nm)
- Topical non-selective beta-adrenergic blockers (1% propranolol cream, 0.5% timolol solution in form of drops or gel).