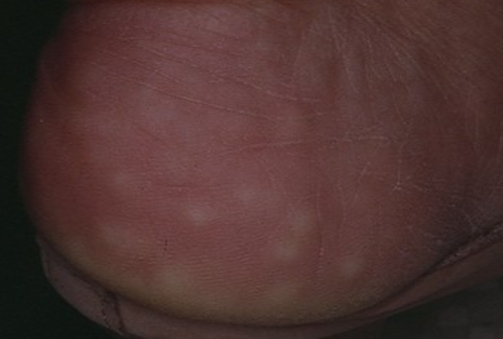
Piezogenic pedal papules is a benign skin condition characterized by soft papules of flesh-colored, white, or yellowish appearance on the heels, occasionally on the wrists. ICD-10 Code: L98.8
The condition is common but often goes undiagnosed due to its asymptomatic nature. It can occur in individuals of all ages, ethnicities, and social groups, with a higher prevalence in women. There is also a pediatric form, known as childhood panniculitis, which occurs in 6% of newborns and young children.
The exact cause of the disease is unknown. The primary mechanism is thought to be herniation of adipose tissue through gaps in the septa of the plantar fascia, which is composed of collagen and elastic fibers. It is more common in individuals who spend long periods of time standing (e.g., workers, salespeople), athletes (e.g., figure skaters, runners, football players), dancers, and those with obesity and flat feet.
Although isolated familial cases have been reported, the hereditary nature of the disease has not been confirmed. Associations have been suggested with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome, probably due to abnormalities in collagen synthesis.This condition is characterized by the appearance of multiple, sometimes solitary, soft or moderately elastic papules, 2 to 10 mm in size, flesh-colored, white or yellowish in color, with a smooth surface. These papules are most prominent when standing, but tend to decrease in size or disappear when lying down or standing on tiptoe. They are usually painless to palpation.
Over time, in chronic disease, the papules may become more firm with mild hyperkeratosis on the surface and may become painful. The eruptions are almost always symmetrical and are located on the medial, dorsal, and lateral margins of the heels and occasionally on the medial surface of the wrists and palms (where they are more prominent when the wrist is flexed or pressure is applied to the palm). Pediatric papules are typically larger and often located on the medial aspect of the heels.- Fibroma
- Lipoma
- Juvenile aponeurotic fibroma (calcifying aponeurotic fibroma)
- Plantar warts
- Epidermal cyst
In most cases, no treatment is needed. For painful papules, the following recommendations may be considered:
First-line treatment: For individuals who are overweight, weight loss is recommended, along with avoiding prolonged standing and limiting physical exertion.
Second-line treatment: Compression stockings or socks, orthopedic shoes to reduce pressure on the heel, electroacupuncture, and intralesional injections of betamethasone mixed with bupivacaine in equal proportions.
Third-line treatment: Papule excision, although recurrence is common.