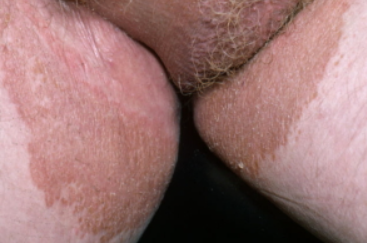
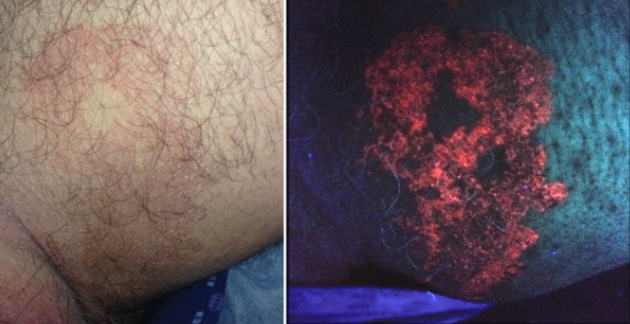
Erythrasma is a chronic bacterial skin disease caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum. ICD-10 code: L08.1.
The causative agent of erythrasma is the gram-positive Corynebacterium minutissimum, which is normally found in the human skin flora. However, under the influence of predisposing factors, this microorganism can show pathogenic properties.
Predisposing factors include increased sweating, high humidity, immune system disorders, diabetes, obesity, and poor personal hygiene. The disease is widespread, but is most common in regions with hot and humid climates. It is more common in males. The contagiousness of the disease is low.Eruptions most commonly occur on the skin of the groin-thigh folds, adjacent to the skin of the thighs, and in the axillary region. Other areas that may be affected include the skin in the folds under the breasts, the abdominal skin, and the interdigital folds of the feet. The eruptions appear as reddish-brown, well-demarcated patches that coalesce to form large affected areas with scalloped edges. Prolonged maceration, peeling and cracking of the interdigital folds is observed, and the condition may be accompanied by pruritus.
Atypical forms of erythrasma include:
- Generalized erythrasma
- Discoid erythrasma
- Vesiculobullous form
- Nail erythrasma
- Palm erythrasma
- Penile erythrasma
Diagnosis is based on the characteristic clinical presentation, detection of the causative organism on microscopic examination of skin scales (gram-positive curved corynebacteria). Culture is not performed and histologic examination is usually unnecessary.
Wood lamp examination
- Tinea versicolor
- Tinea corporis and intertrigo
- Psoriasis
- Candidal intertrigo
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Pityriasis rotunda
Systemic antibiotics:
- Erythromycin 0.25 g orally four times a day for 14 days, or
- Tetracycline 0.25 g orally four times a day for 14 days, or
- Clarithromycin 2 tablets of 500 mg as a single dose.
For localized lesions in skin folds:
- Fusidic acid cream 2% applied topically twice a day for 2 weeks, or
- Erythromycin 5% ointment applied topically twice a day, rubbed into the affected areas for 7 days, or
- Clindamycin 2% cream applied topically twice a day to the affected areas for 2 weeks, or
- Mupirocin 2% ointment applied topically twice a day to the affected areas for 2 weeks, or
Management of treatment failure: Prescribing a drug from another pharmacologic group.
Prevention: Elimination of excessive sweating and observance of personal hygiene rules. During the treatment it is necessary to disinfect the patient's clothes, underwear.