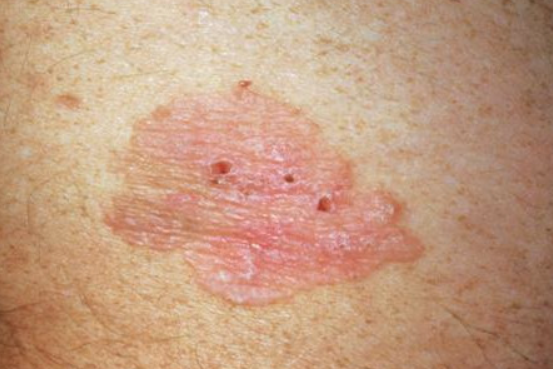
Bowen disease is an intraepidermal neoplasm that, in most cases, remains carcinoma in situ. It is classified under the ICD-10 code D04.9.
It typically occurs in older individuals and affects men and women equally. Bowen disease is more common on sun-exposed areas of the skin. In addition to actinic factors, arsenic compounds, hydrocarbons, and mustard gas are considered carcinogens.
The following clinical variants have been identified:
- Annular
- Verrucous
- Pigmented
- Bowen disease of the nail bed
It is characterized by the presence of a single, sharply demarcated, plaque-like lesion. The lesion grows slowly at the periphery with a more active, slightly elevated border. The border may be scaly or crusted. The lesion has a round or oval outline, but occasionally it may have an irregular shape. The surface is rough and granular, sometimes slightly verrucous. Superficial erosion and ulceration may occur, resulting in partially scarred and enlarging ulcers.
The most common sites are the trunk, upper extremities, and groin.
- Viral warts
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Paget's disease
- Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
- Lentigo maligna melanoma
- Actinic keratosis
- Tinea corporis
- Psoriasis
- Lichen simplex chronicus
Treatment options include surgical excision, laser ablation, cryotherapy, and cytostatic agents such as 1-2-5% fluorouracil ointment applied topically twice daily for 1 week, followed by a 1-week break and repeated courses (total of 4-6 courses).
Prognosis: The frequency of transformation of Bowen disease to invasive squamous cell carcinoma varies from 11% to 80% according to different authors.