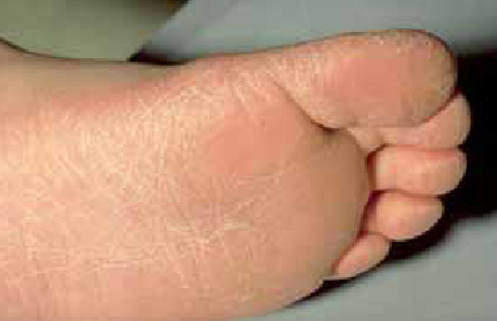
Juvenile plantar dermatosis is a childhood dermatosis characterized by erythema, scaling, and painful cracks in the area of the soles. ICD-10 code: L98.8.
The disease is most common in prepubertal children, but can also occur in adults. The average age of onset is 7 years, and remission usually occurs by age 14.
This condition is commonly observed during the fall and winter seasons when children wear warm socks, waterproof shoes, or rubber boots. It is more common in children with atopic dermatitis. The condition develops due to excessive sweating of the feet in tight-fitting shoes, followed by rapid drying in environments with low humidity.
It presents as erythema and scaling of the weight bearing areas of the sole. The sole surfaces show scaling, erythema and cracking, with tenderness being one of the symptoms. The skin of the plantar surface becomes dry, erythematous, scaly, and fissured, especially in areas subjected to the most pressure from body weight (toes and metatarsal regions).
Children complain of pain and discomfort, which may be more severe than itching. The cracks may be deep and very painful, extending to the lateral surfaces of the toes. In some cases, the entire sole may be affected symmetrically. Inflammation may be limited to certain areas of the sole. Fine and deep cracks may appear as the disease progresses.
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Tinea pedis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
To manage this condition, feet should be kept dry and prolonged use of moist, constricting footwear should be avoided. Applying a thick emollient ointment such as "Aquaphor" or "Aveeno" several times a day is recommended. If pruritus is present, group II or III topical steroids may be applied twice daily for 2-3 weeks, preferably at night under polyethylene occlusion.
Fifteen-minute tar oil baths may be helpful, followed by application of emollient ointment or topical corticosteroids.
Preventive measures include changing into light leather shoes after removing wet boots, wearing shoes that allow the feet to dry, and frequently changing socks if they become moist.