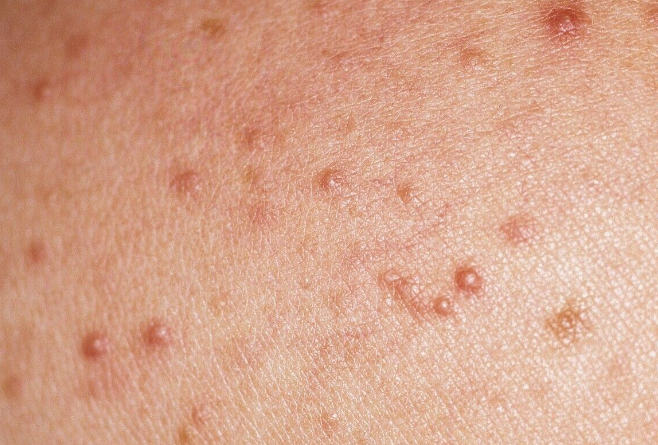
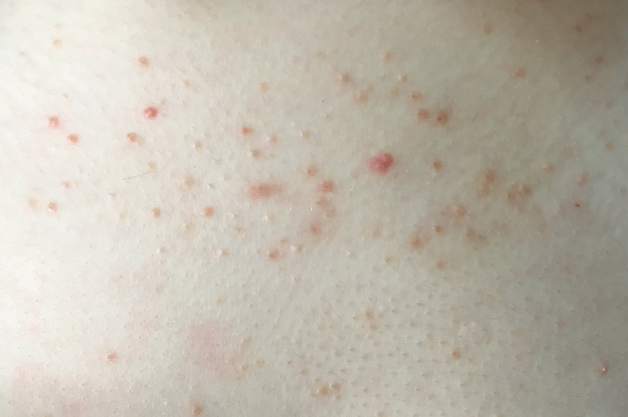
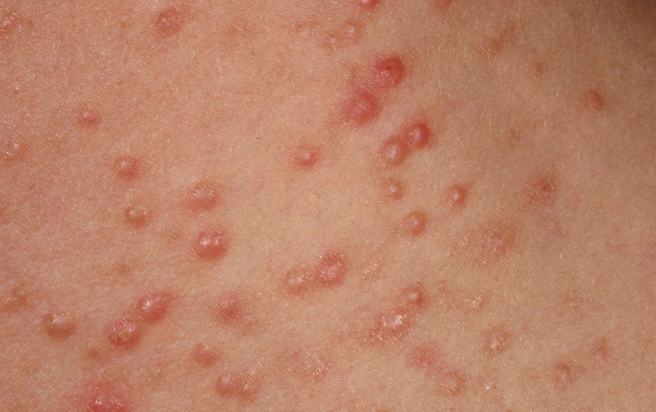
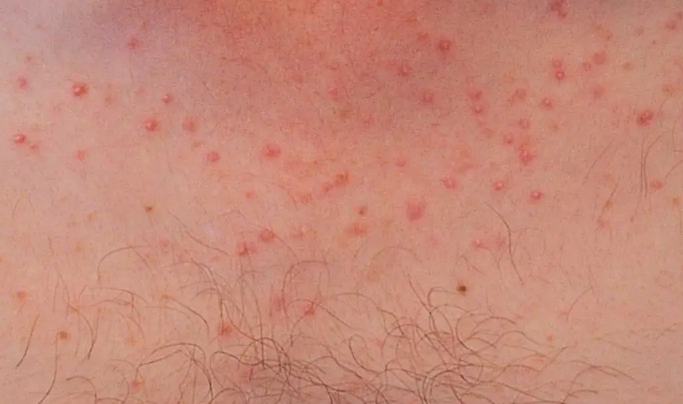
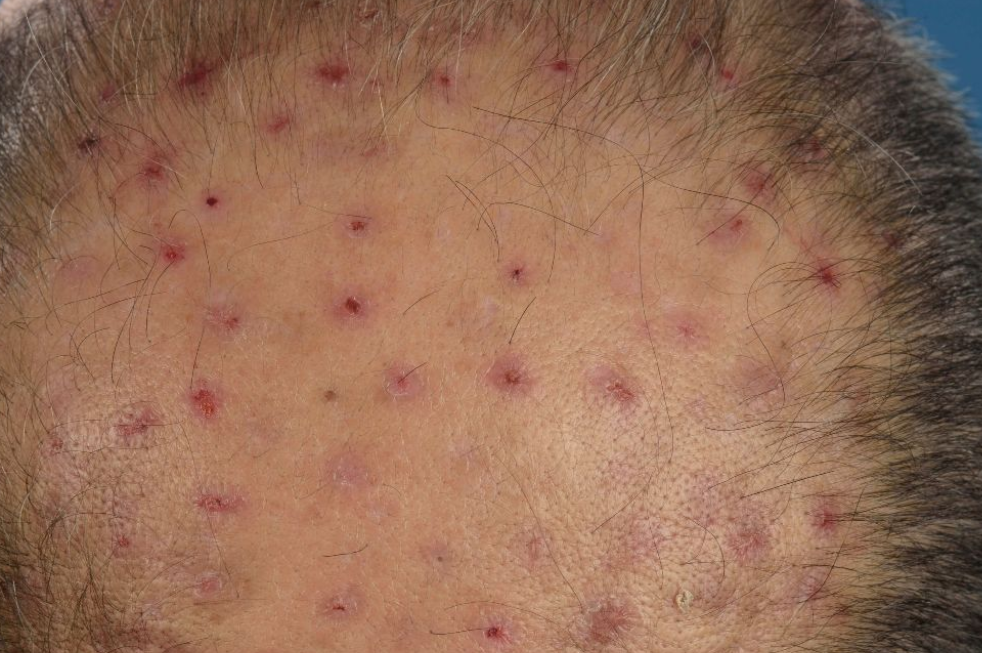
Acneiform eruptions are a group of disorders characterized by the presence of eruptions similar to those seen in acne vulgaris, but with different etiologic and pathogenetic mechanisms.
The etiology of drug-induced acne varies depending on the specific drug involved. Mallorca acne or acne aestivalis is caused by excessive amounts of fatty bases in sunscreens and exposure to UV radiation. Pityrosporum folliculitis is caused by fungi of the genus Pityrosporum ovale. Acne necrotica (varioliformis) is a rare, chronic and recurrent condition of unknown etiology.
Classification:- Drug-induced acne can be classified into various types, including:
- Halogen-induced acne (bromide acne, chloracne, iodide acne)
- Corticosteroid-induced acne
- Androgen-induced acne
- Acne caused by the use of medications for thyroid disorders
- Doping-induced acne (caused by the use of anabolic drugs and B-group vitamins)
- Acne caused by the use of cytostatic, immunotropic, anticonvulsant, antituberculosis drugs, and others
- Mallorca acne
- Pityrosporum folliculitis
- Varioliform acne
- Sudden onset within a few days
- Widespread distribution of the eruptions
- Atypical localization
- Unusual age for acne vulgaris
- Presence of monomorphic eruptions (papules or papulopustules) at the same stage of development.
Drug-induced acne
Mallorca acne
Pityrosporum folliculitis
Varioliform acne
The diagnosis is based on the characteristic clinical picture and the results of laboratory tests.
Mandatory laboratory tests include:- Blood biochemistry (total bilirubin and its fractions, triglycerides, ALT, AST, cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, glucose).
- Assessment of hormonal status in women with clinical signs of hyperandrogenism (FSH, LH, free testosterone fraction, etc.)
- Identification of the microbial flora on the skin with determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics
- Complete blood count.
- Acne vulgaris
- Perioral dermatitis
- Keratosis pilaris
- Rosacea
- Bacterial folliculitis
- Eosinophilic folliculitis
- Pseudomonas folliculitis
For drug-induced acne (including steroid acne), discontinuation of the medication that caused the condition is recommended. If discontinuation of the drug is not possible, the following treatment options are prescribed:
- Oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 10-14 days + topical adapalene once daily for 3-6 months, or
- Topical isotretinoin applied in the evening once daily for 3-6 months, or
- Topical azelaic acid 1-2 times daily for 3-6 months (continuous use may be possible) + benzoyl peroxide 2.5-10% solution applied topically to inflammatory lesions 1-4 times daily for 8-12 weeks.
For Mallorca acne, it is necessary to avoid sun exposure and the use of greasy sunscreens. In addition, the following treatments are prescribed:
- Topical isotretinoin applied in the evening once daily for 3-6 months, or
- Low-concentration tretinoin (0.025%) or
- Topical benzoyl peroxide 2.5-10% solution applied to inflammatory lesions 1-4 times daily for 8-12 weeks.
- Oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 3-4 weeks, or
- Oral tetracycline 500 mg twice daily for 3-4 weeks.
For Pityrosporum folliculitis, it is recommended to wash the scalp with a shampoo containing ketoconazole. In addition, the following treatments are used:
- Ketoconazole 200 mg once daily for 10 days + topical clotrimazole 2% cream applied twice daily for 14-21 days.
For varioliform acne:
- Oral tetracycline 500 mg twice daily for 2-3 months, or
- Oral erythromycin 500 mg twice daily for 2-3 months + topical clindamycin 1% gel applied twice daily for 2-3 months, or
- Topical erythromycin 1-5% solution as compresses applied twice daily for 2-3 months + topical benzoyl peroxide 2.5-10% solution applied to inflammatory lesions twice daily for up to 4 months.
- Oral isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5-1 mg/kg (maximum daily dose 60-80 mg) once daily for 2-4 weeks. Thereafter, the dose is gradually reduced (cumulative dose should not exceed 150 mg/kg). The total duration of treatment is 4-6 months. Monthly monitoring of blood biochemical parameters (bilirubin, ALT, AST, triglycerides, cholesterol) is mandatory before starting the medication and during treatment.
Complications and Side Effects of Treatment
Women of reproductive age should be informed about the teratogenic effect of isotretinoin, which persists throughout the entire duration of medication intake and for 1 month after completing the treatment. When using azelaic acid, the possible occurrence of erythema and burning sensation is possible.
Errors and Unjustified Prescriptions
They may be due to an incorrect diagnosis.