Lichenoid keratosis (lichen planus like keratosis) is a benign skin condition associated with marked inflammatory changes that resemble lichen planus. It occurs in 85% of cases between the ages of 35 and 65, and very rarely in children. Women are three times more likely to be affected than men.
The pathogenesis of lichenoid keratosis is not fully understood, but it is thought to be an inflammatory reaction that occurs in the setting of a pre-existing solar lentigo, seborrheic or actinic keratosis. Mutations in the FCFR3, PIK3CA, and RAS genes found in 50% of biopsies, which are also seen in seborrheic keratosis and solar lentigo, suggest that keratosis is a regressive variant of these conditions.
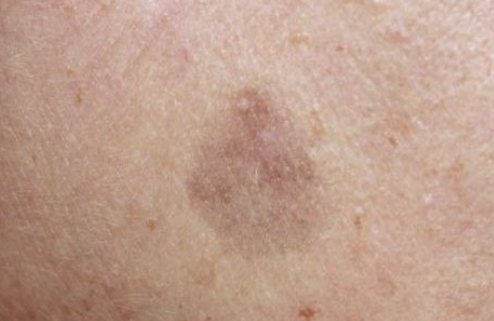
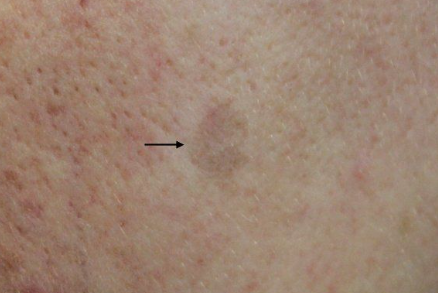
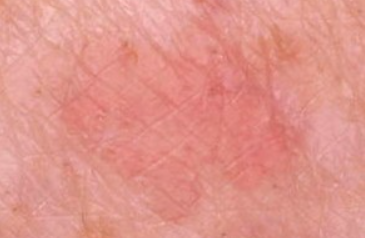
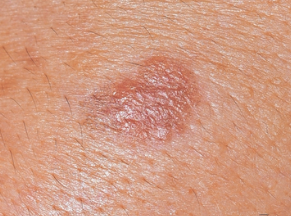
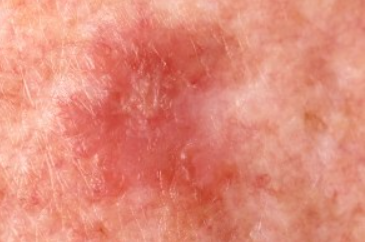
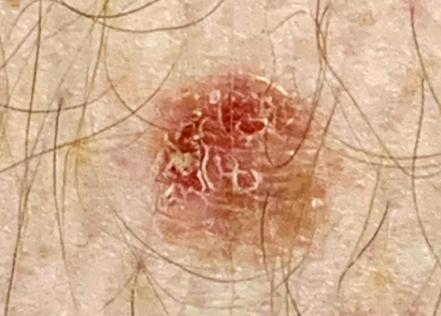
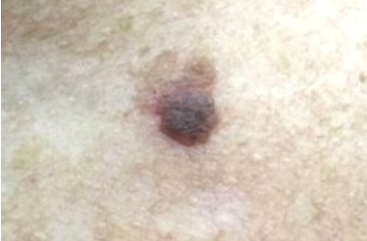
The disease is characterized by the appearance of a single flat papule ranging in color from pink to reddish brown and purple, with a diameter of 3 to 19 mm. The papules are often preceded by the eruption of purple or hyperpigmented patches. The surface of the papules is often scaly, but may be smooth or hyperkeratotic. Wickham's striae are absent.
In many cases, the papules are located near areas of solar lentigo, seborrheic, and actinic keratosis. The lesions are typically found on sun-exposed parts of the body, most commonly on the forearms and upper trunk, and less commonly on the face, neck, and shins.
The eruptions are usually asymptomatic, but in some cases patients may experience mild itching and burning. In rare cases, the eruptions may be multiple. Sometimes the disease presents as single gray, pink-gray, or gray-brown spots, 2-3 mm to 1-3 cm in diameter, with a scaly surface.
The course is chronic, but spontaneous regression of the papules is often observed several months after the onset of the disease, leaving behind atrophic hypopigmented scars.
Flat pigmented type
Flat erythematous type
Plaque-like type
Morpheaform type
Papulo-keratotic type
Nodular type
- Actinic keratosis
- Lichen planus
- Bowen disease
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Bowenoid papulosis
- Melanoma
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Melanocytic nevus
Once lichenoid keratosis has been diagnosed, no further therapy is recommended as the condition is benign. For cosmetic purposes, PUVA therapy, retinoids, and topical calcipotriol may be used.