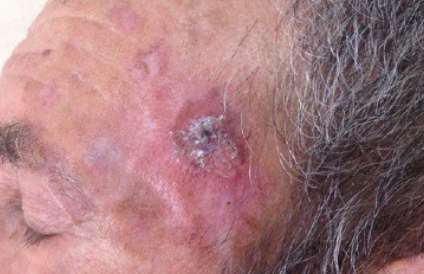
Inverted follicular keratosis (IFK) is a rare benign tumor of the follicular infundibulum. ICD-10 code: L11.0
It can occur at any age, but 80% of cases occur in people over 50 years old, and it is twice as common in men.
There is no unanimous consensus on whether this neoplasm should be considered a separate nosologic entity.
Some authors consider it a variant of seborrheic keratosis or an infundibuloma, while others point to its endophytic growth, which is not observed in seborrheic keratosis, and certain clinical features, although not very significant.
It is characterized by the appearance of a painless, solitary, firm, pinkish-red, grayish, or flesh-colored papule up to 10 mm in diameter, rarely larger. In some cases, exophytic growths with a papillomatous surface in the form of a cutaneous horn or a papule with uneven pigmentation mimicking malignant melanoma may be observed. In 85% of cases it is localized on the face (cheeks and upper lip, less frequently on the chin, forehead, nasal wings, eyelids), very rarely on the hairy part of the head, neck or extremities.
Clinically, it is not easy to identify, and more often it is subjected to histologic examination with diagnosis of vulgar or seborrheic wart, keratopapilloma or, less frequently, basal cell carcinoma if ulceration occurs. Multiple lesions have been observed in patients with Cowden syndrome, and in one of these cases, keratosis was a presenting feature. No cases of malignancy have been reported.
- Warts
- Keratopapilloma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Keratoacanthoma
- Eccrine poroma
Electrocautery and surgical excision are recommended treatments. Recurrence after surgical excision is extremely rare.
The prognosis is favorable.