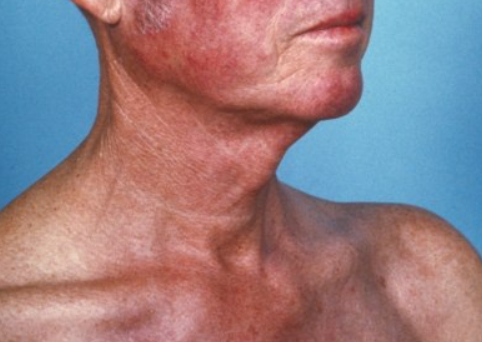
Carcinoid syndrome is an episodic intense flushing of the face, neck, and upper trunk. ICD-10 Code: E34.0
Carcinoid syndrome is caused by the release into the bloodstream of vasoactive mediators secreted by carcinoid tumors. Most carcinoid tumors originate in the small intestine, often in the appendix. The vasoactive mediators released by the tumor are inactivated in the liver before entering the bloodstream.
When carcinoid tumors metastasize to the liver, vasoactive mediators are released into the bloodstream. Carcinoid tumors also occur in the lungs and release mediators into the bloodstream.
Carcinoid syndrome manifests as acute flushing of the face, neck, and chest lasting approximately 30 minutes. Flushing is often associated with difficulty breathing, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Carcinoid syndrome may be associated with internal carcinoid tumors of the bronchi or small intestine with liver metastases. The course and prognosis usually depend on the associated internal malignant process.
The level of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in urine is elevated 24 hours after urine collection.
Patients with skin manifestations suggestive of internal malignancy without known signs of such disease require a thorough evaluation.
- Rosacea
- Erysipelas
- Pellagra
- Idiopathic craniofacial erythema
- Alcohol flush reaction
- Phaeochromocytoma