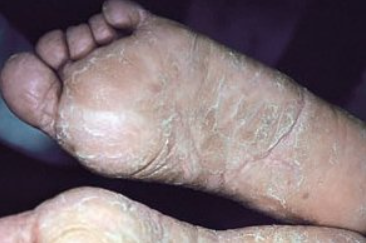
Keratoderma climactericum is an acquired diffuse keratoderma of the palms and soles that develops in women during menopause. ICD-10 Code: L85.8
It occurs in women over the age of 45. The etiology and pathogenesis are unclear. Haxthausen, the first researcher to describe the disease, associated keratoderma with the so-called "climacteric triad" - hypertension, obesity and arthritis.
The role of sex hormones in the pathogenesis of the disease has not been definitively established. In one study of 10 affected women, levels of estradiol, estrone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone were within the normal range. However, in another study, keratoderma developed in young women after oophorectomy and resolved with estrogen replacement therapy. Some believe that a decrease in collagen content in the skin, influenced by sex hormone levels, may contribute to the development of keratoderma.
The disease begins with appearance of round or oval areas of yellowish hyperkeratosis at pressure points on the soles, often in heel area. As the disease progresses, hyperkeratotic patches coalesce to form extensive areas of indistinct involvement covered by a thick layer of yellow-brown keratotic masses. Painful erythematous fissures develop, making walking difficult.
Palms are less commonly involved. Initially, a yellowish-gray area of hyperkeratosis appears in the center of the palm and slowly spreads over the entire palm with formation of fissures.
Characteristically, lesions do not spread beyond the palms and soles. Itching is mild and infrequent. The condition worsens in winter. Obesity and the wearing of open shoes contribute to the progression of the disease.
- Palmoplantar psoriasis
- Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis
- Paraneoplastic keratodermas
- Secondary syphilis
- Reiter's syndrome
- Drug-induced keratodermas
- Hyperkeratotic eczema
- Tinea pedis
Treatment may include:
- Retinoids (etretinate, tigason, acitretin) orally at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg per day for 6-8 weeks.
- Topical treatment with 0.05% estradiol cream and/or preparations containing 25-40% urea.