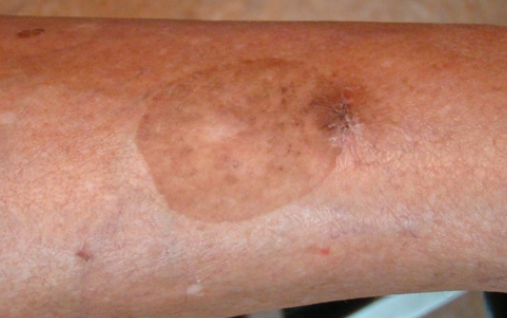
Large cell acanthoma is a benign epithelial tumor characterized by the clinical presentation of mostly solitary pigmented patches on exposed areas of the body. ICD-10 code is D23.9.
The condition is observed in individuals between the ages of 28 and 89, with an average onset of 50-60 years. It is more common in women of European descent. Due to its often asymptomatic nature, the exact prevalence is unknown as the condition is often ignored or misdiagnosed. According to one study, the incidence is 2.5 per 1000 skin biopsies.
The etiopathogenesis is unknown. Many authors consider it a variant of actinic keratosis, solar lentigo, senile keratosis, or Bowen's disease. UV radiation is thought to play an important role in the pathogenesis. Genetic studies show a low degree of aneuploidy typically associated with malignant tumors. Nevertheless, large cell acanthoma is classified as a benign neoplasm. Human papillomavirus type 6 has been detected in lesion tissue in some studies, but its exact role in the pathogenesis of the disease is not well defined.
In typical cases, the condition presents as a solitary pigmented spot, flat papule, or plaque with clear borders. These lesions may be oval, round, or irregular in shape with a scaly surface. In some cases, the coloration of the elements is uneven, and both papules (nodules) and spots may appear in the same focus. Sizes range from 5 to 20 mm (average 10 mm), rarely larger. Localization often occurs on exposed areas of the body such as the face, neck, upper chest and back, forearms, and shins.
Clinical variants include
- Multiple form - primarily observed on limbs as multiple small lesions of uniform size.
- Hypopigmented form - characterized by single or multiple lesions ranging from flesh-colored (white) to pink.
- Ocular form - lesions in the eyelid and conjunctival area.
- Solar lentigo
- Benign lichenoid keratosis
- Clear cell acanthoma
- Pigmented actinic keratosis
- Amelanotic melanoma
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Flat warts
- Nummular eczema
Treatment involves surgical excision. There are reports of successful topical application of tretinoin cream in combination with 10% urea cream.