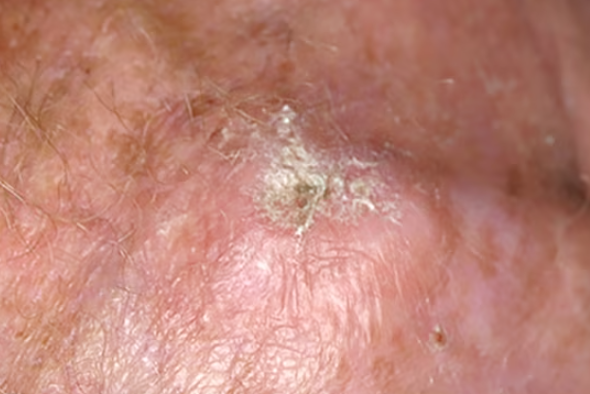
Actinic keratosis is a benign neoplasm that primarily occurs on exposed areas of the skin in elderly individuals. It may be considered an early form of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. It is classified under the ICD-10 code L57.0.
Actinic keratosis typically occurs in individuals over the age of 50 and develops as a result of prolonged cumulative exposure to UV radiation on sun-exposed areas of the skin. The affected areas are predominantly located on the face and the back of the hands, and less commonly on the lower third of the forearms.
The following variants are distinguished based on histopathological examination:
- Hyperkeratotic.
- Atrophic.
- Bowenoid.
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Chondrodermatitis
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Discoid lupus erythematosus
Treatment options include cryotherapy (double application of cryoprobe for 5 seconds), laser destruction. Cytostatic agents such as 1-2% fluorouracil cream may also be used. It is applied topically twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 1-week break and repeated for a total of 4-6 courses.
The use of photoprotective creams is necessary to prevent the development of actinic keratosis.
Prognosis: Actinic keratosis occasionally can transform into squamous cell carcinoma, less frequently into basal cell carcinoma.