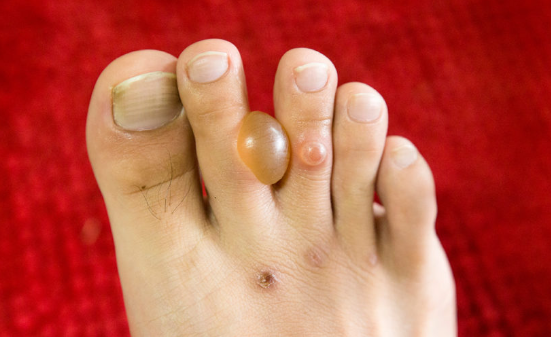
Diabetic Bullae (bullosis diabeticorum) is a dermatosis occurring in patients with diabetes and characterized by the appearance of subepidermal blisters. ICD-10 code: E13.6
This condition occurs in 0.5% of diabetes patients aged 17 to 79 years (average age of 55 years), and is more common in males than in females (2:1). The etiopathogenesis is unclear, but microangiopathy and local metabolic disturbances are thought to play a role. The blister cavity is localized in the lamina lucida, and antibodies to type IV collagen are detected.
Blisters with a thick base appear suddenly and spontaneously on apparently healthy skin without prior inflammation. They range in size from 1-2 mm to 3-5 cm and contain a clear, viscous fluid. The eruptions are mainly localized on the feet and legs, but may also occur on the dorsum of the hands, fingers, and forearms. There are usually no subjective symptoms. Bullaes disappear spontaneously without scarring within 2-5 weeks. Recurrences may occur over several years.
The diagnosis is based on the patient's medical history, the presence of diabetes, and the clinical picture.
- Insect bites (including bites from bugs and fleas)
- Contact dermatitis
- Poison ivy
- Bullous fixed drug eruption
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Bullous cellulitis
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Porphyria cutanea tarda and pseudoporphyria
- Friction blister
- Bullous form of erythema multiforme
- Bullous impetigo
- Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Treatment includes normalizing blood glucose levels and prescribing topical antibacterial agents to prevent secondary infection.